Todd-AO: How it Started |
Read more at in70mm.com The 70mm Newsletter |
| Written by: Thomas Hauerslev. All pictures from the Optical Heritage Museum archive, Southbridge, CT, USA. Presented as a lecture at the Todd-AO Festival, Schauburg Cinerama, 30. September 2018 | Date: 13.05.2021 |
 After
three years of research, development and production, "The Greatest Show in
Todd-AO" finally
opened in October 1955 at the Rivoli Theatre,
Broadway, New York City, USA. After
three years of research, development and production, "The Greatest Show in
Todd-AO" finally
opened in October 1955 at the Rivoli Theatre,
Broadway, New York City, USA.What is the Todd-AO Process? Well Todd-AO, is razor sharp 70mm film, projected at 30 frames per second on BIG screens. 70mm film with rock-steady picture quality is very impressive, thanks to the large image area - and the high frame rate. The negative is 4 times larger than standard 35mm widescreen film. The Todd-AO process sat the standard for 65mm and 70mm film - - and inspired the film industry for 50 years. The 70mm film format is often associated with the big epics and musicals from the 1960s. The beginning of Todd-AO dates back to the summer of 1952 when my story begins. 60 years ago Mike Todd convinced American Optical Company to take part in the development of the first new film system in more than 2 decades.
Before I go into that, I have to explain a phenomenon known as “peripheral
vision”. In order to understand depth and distance, our mind is dependent on
what the eyes sees to the sides, rather than just straight ahead. This is
how the principle works in the cinema. |
More in 70mm reading: Todd-AO: Wie alles begann Počátky Todd-AO TODD-AO PROCESS • Films | Premiere • People | Equipment • Library | Cinemas • Distortion Correcting • DP70 / AAII Projector • Todd-AO Time Line • Who developed Todd-AO in70mm.com News Peripheral Vision, Scopes, Dimensions and Panoramas in70mm.com's Library Presented on the big screen in 7OMM 7OMM and Cinema Across the World Now showing in 70mm in a theatre near you! 70mm Retro - Festivals and Screenings |
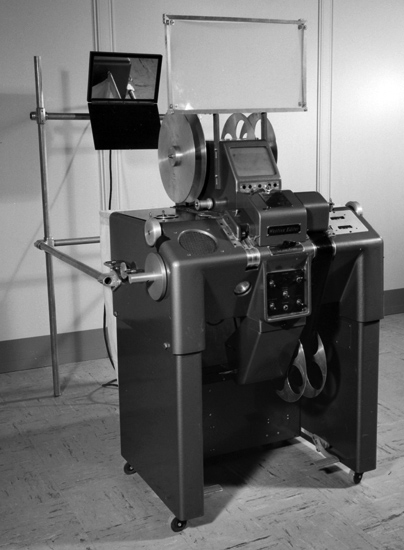 Westrex
Todd-AO
editing machine. Westrex
Todd-AO
editing machine.Fred Waller, inventor and engineer, experimented with peripheral vision and tried, with success, to copy human vision with film. His invention Cinerama, very effectively created an illusion of reality, by filming an extreme wide-angle panorama on three strips of film. When a spectator sits somewhere close to the center of the circle, looking at the screen, he’s having a First Person Experience. He’s having a sensation of participation. The first person experience was the whole point of wide-angle lenses and curved screens. Cinerama duplicates this sensation of participation in a very complicated projection process with three projectors locked together, showing three 35mm films side by side, on the same curved screen, at the same time. In theory, the three images are seen on the screen, as one large complete undistorted image. There is some movement between the panels, however, and this image instability is extremely visible where the three images meet, at the two join lines. This instability destroys the illusion, and audience participation is completely destroyed. Cinerama was very expensive to install, because cinemas often had to be rebuilt substantially. In some cases, several hundred seats were unusable because of the screen and additional projection equipment required to show Cinerama. Michael Todd, one of the key people behind Cinerama realized the technical limitations, and that it didn’t have the versatility for storytelling. Fred Waller assured him the technical shortcomings would be fixed before the premiere of the first film but the join lines were never removed. "This is Cinerama" demonstrated what could be done with this new technique when it premiered in New York 30 September 1952 and it was a tremendous box-office success. Mike Todd left the theatre not satisfied with Cinerama, and set himself a new goal – to perfect the illusion of reality, and do it less complicated. |
|
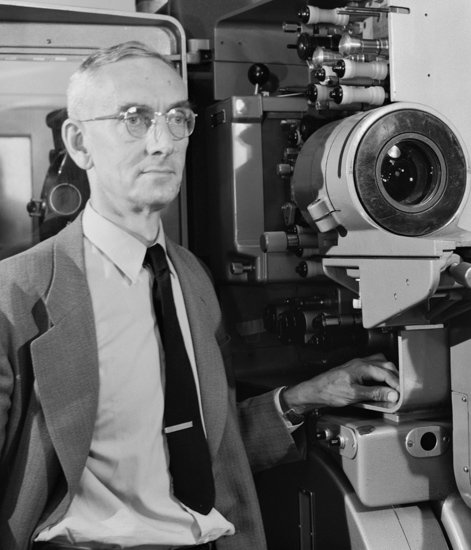 Dr.
Brian O'Brien, Head of Research and Development for American Optical
Company, next to the Todd-AO
"all purpose" 70mm projector installed at American Optical Research Center's
"half-scale" Todd-AO demonstration theatre. Dr.
Brian O'Brien, Head of Research and Development for American Optical
Company, next to the Todd-AO
"all purpose" 70mm projector installed at American Optical Research Center's
"half-scale" Todd-AO demonstration theatre.Two weeks later, on 15 October 1952 Mike Todd reached Dr Brian O'Brien, THE optical wizard of America at that time, and asked him for a meeting. The meeting, which took place in a bar across Rochester airfield, was witnessed by Walter Siegmund, one of O'Brien's assistants and according to him, Todd outlined the problem on a napkin and asked if Cinerama could be simplified. Mike Todd's concerns were part economy – he wanted to be able to put the new process into any existing theatre, without too much expensive rebuilding and part technology – getting rid of the join lines. He wanted to develop a system of motion picture photography with a single camera and a single projector, to project a Cinerama-like image, free of obvious defects, onto a curved screen. According to the legend, Mike Todd asked Dr. O'Brien:
Brian O'Brien explained that such an undertaking would require a large optical specialist like Eastman Kodak, Bausch & Lomb or American Optical Company. Dr. O'Brien sent his assistant Walter Siegmund to New York to see “This is Cinerama” who enthusiastically reported to Dr. O'Brien in one word “WOW”.
Mike Todd called Dr. O'Brien a month later to tell him, that he had settled
for American Optical Company. O'Brien asked Todd to come to Southbridge the
following Sunday to have lunch with Walter Steward, the president of
American Optical Company. Mike Todd pitched the idea of “a Cinerama out of
one hole” to the American Optical Company's Walter Steward. He did it so
well, that Steward told him, that if Todd could put together a group of
people, who were all well known in the movie industry and come up with the
finance to develop this process, the American Optical company would go for
it. Todd assured him that finance and people was no problem and the first
film was going to be the Broadway play “Oklahoma!”. Todd had approached
Rodgers and Hammerstein and sweet-talked them into selling him their most
valuable asset; and producing their play in the new process, which would
“have the impact of Cinerama but none of its limitations”.
|
|
 Todd-AO
splicer Todd-AO
splicerMike Todd formed “Magna Theatre Corporation” the following Friday, 27 November 1952 and commissioned American Optical Company to develop the lenses, camera, projector, light source for the projector and the very bright screen they envisioned, and of course the sound system. The initial group of engineers consisted of Brian O’Brien, Walter Siegmund, John Davis and Robert E. Hopkins. Their job was to get an understanding of the problem they were asked to solve. What kind of distorting was involved in wide-angle projection and how to lay out the basic geometry of screen? To match Cinerama's three 35mm films;, they needed more real estate on the film and had to adapt some old Thomascolor 8-perf 65mm cameras. 35mm film was simply inadequate to get enough light through the gate of the projector. The decision to go with 5 holes was dictated by the width and height parameters of the screen that had to go into existing proscenium arches and an approximately 2:1 aspect ratio. The curve was chosen to enhance the audience participation effect and to reduce fish-eye distortion. A lot of experimentation with screen shapes, sizes and materials was done. Essentially the screen should not impose on your vision – it should be invisible – a kind of a window to the world. A typical Todd-AO screen measured 15 by 7m with a curve depth of 4 meters. The distance from side to side along the curve measured 18 meters. These first decisions were made by this small group of people who sat together thinking:
|
|
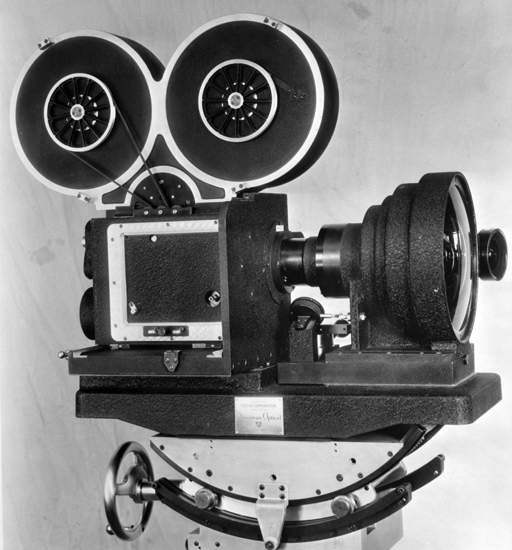 Prototype
Todd-AO camera with the 128 dgr "Bug Eye" lens. Prototype
Todd-AO camera with the 128 dgr "Bug Eye" lens.Film speed was increased to 30 images per second to smoothen out strobing, or flicker, which can be very annoying in bright scenes and especially on a huge screen. It was decided to add another 5 millimeter to the release print to accommodate the stripes of magnetic oxide, on which the sound should be recorded on the positive 70mm print. The Todd-AO multipurpose projector was developed by the American Optical Instrument Division in Buffalo and manufactured by the Philips company in Holland. The Todd-AO projector, or the DP70 which became the popular name, was designed to be compatible with any motion picture system and the quality of this machine is unsurpassed to this day. It is still considered by many as the Rolls-Royce of film projectors. Mr. Kotte, the chief designer, was honored with an OSCAR for the development of the DP70 in 1962. The cameras were co-developed with Mitchell Camera Corporation. The sound system was developed in corporation with Altec who also equipped cinemas with their “Voice of the theatre” speakers. Ampex Corporation developed playback technology, including soundheads. Everything was made to strict specifications set by the Research & Development department of American Optical Company. Westrex Recording developed sound recording, mixing and editing equipment which was defined as 6-channel magnetic stereo with 5 discrete screen channels and 1 effects channel. The frequency range had to be 20 – 18.000 Hz. |
|
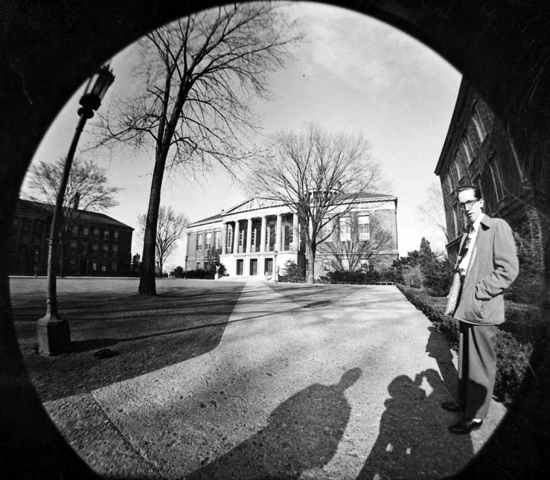 Still
photo made with 128 dgr "Bug Eye" lens at University of Rochester. Note the
curving tree and lamp post from the natural distortion in a fish-eye lens. Still
photo made with 128 dgr "Bug Eye" lens at University of Rochester. Note the
curving tree and lamp post from the natural distortion in a fish-eye lens.
In early 1953 work began on the signature lens, the 132 degree field of view lens, nicknamed “The Bug Eye”. It was quickly realized, however, that narrower angle lenses were also needed. So, a lens with a field of view of 64 degrees was also developed by AO. Two lenses of 42 and 37 degrees were purchased off-the-shelf and adapted with standard lens mounts. • 42 degrees = 55mm Zeiss, F2 Biotar double Gauss • 37 degrees = 76mm Voigtländer or Schneider F2,8 Heliaor for 6x6 photography 128° (22mm), 64° (44mm), 48° (58mm) & 37° (76mm). Most of "Oklahoma!" was filmed with German lenses. By June 1953 the AO engineers had the first prototype camera and lens ready for testing. These tests took place at the “Atom Smasher” rollercoaster at Far Rockaway play land on Long Island. Mike Todd wanted to duplicate the rollercoaster ride from “This is Cinerama” by filming the same coaster with the new equipment. Later, in September 1953, Mike Todd and Harry Stradling, went to Europe with the new equipment to film scenes for a demonstration film. By this time, when the work had reached the exploitation stage, the process was named “Todd-AO” by combining Michael Todd's last name and the initials of American Optical. The Todd-AO Corporation was formed in 1953 to be the technical agent for the process and to supply and service the necessary equipment for the theatres and filmmakers. The company was owned by Magna Theatre Corporation and American Optical Company, which also owned all process patents and then licensed them to The Todd-AO Corporation. |
|
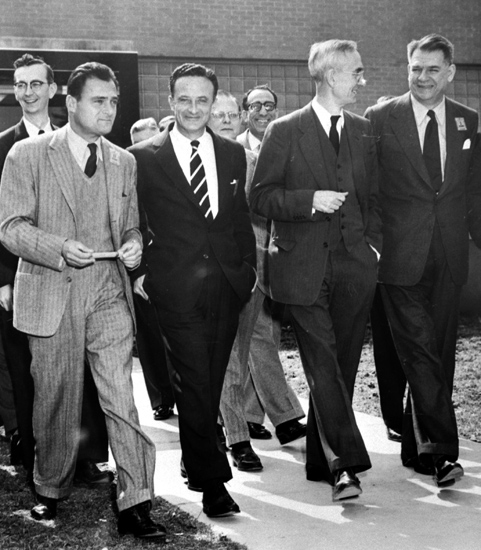 Front
row left to right: Mike Todd, Fred Zinnemann, Dr. Brian O'Brien, and Oscar
Hammerstein II. Brian O'Brien Jr. seen behind and to the left of Mike Todd. Front
row left to right: Mike Todd, Fred Zinnemann, Dr. Brian O'Brien, and Oscar
Hammerstein II. Brian O'Brien Jr. seen behind and to the left of Mike Todd.The greatest show in Todd-AO: The 800 seat Regent Theatre in Buffalo, NY was used as a demonstration cinema for Todd-AO. One of the first screenings of prototype Todd-AO for a very select audience took place on 8 August, 1953 – only 9 months after the formation of MAGNA. It was time to demonstrate Todd-AO's ability to duplicate Cinerama, without its defects, for Rodgers and Hammerstein, the boards of Magna and Todd-AO, plus some industry insiders. This demonstration was important. If R&H didn’t like what they saw, Magna had no film to produce in the process and the finance would probably disappear. Mike Todd proudly coined the slogan on the spot.
Scenes with young couples on a picnic and seven women in bathing suites delighted Rodgers and Hammerstein.
[We owe our thanks to these girls]. The
demonstration was a success and Rodgers and Hammerstein decided Todd-AO had
the visual scope and depth they needed, and sold the “Oklahoma!” movie
rights to Magna, for a million dollars and 40% of the movie profits. |
|
Distortion Correction Printing |
|
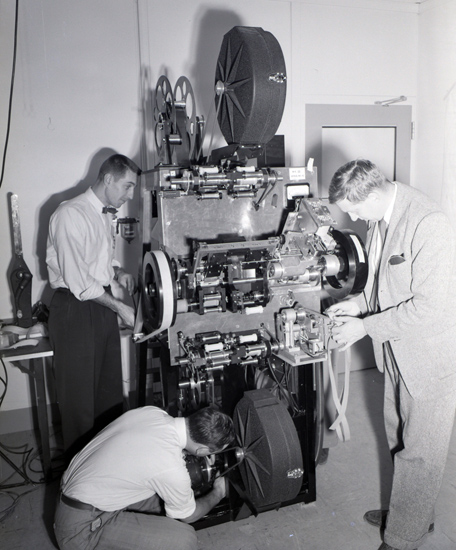 Todd-AO
staff dressed in suit and tie working with the Todd-AO Mark
III printer in Fort Lee, New Jersey. Walter Siegmund to the right. Todd-AO
staff dressed in suit and tie working with the Todd-AO Mark
III printer in Fort Lee, New Jersey. Walter Siegmund to the right.One of the most unique features of the process was the "Distortion Correcting Printing Process". Mike Todd’s original idea was to be able to show Todd-AO in any theatre without expensive rebuilding. Typically, projectors had to be installed in existing projection facilities at the very top of the cinema, resulting in serious image distortion, coming from the extreme downward projection angle. The distortion correction printing processes dealt with that problem, by optically distorting the image on the frames on the film strip. When projected, the distorted frames would “unfold” into a perfect image. The printer corrected three types of distortion: • Bug Eye lens distortion • Screen curvature • Down angle projection The process worked as it was supposed to do, but only in Todd-AO and eventually it was abandoned, when all printers were scrapped. “Oklahoma!” premiered at the Rivoli Theatre 13 October 1955 and received very favorable reviews, but the first presentation was flawed by a print not manufactured to be shown for a paying audience. It turned out, that the original negative had been scratched in Hollywood. Those scratches didn’t make any difference with a normal wet-gate contact print. But since the Rivoli print was made with the distortion correction printer, which was a continues projection printer, scratches of this nature meant that even the smallest negative scratch showed up on the screen. The premiere in Hollywood two months later, was the perfect show, as contact prints were used. The Todd-AO premiere of “Oklahoma!” concluded three years of hard work, involving more than one hundred engineers from American Optical Company, Ampex, Westrex, Mitchell and Philips. American Optical Company developed the Todd-AO process and established the standard for 65mm and 70mm film with 6-track stereophonic sound. The industry adopted the format, and soon, other camera and projector manufacturers made new equipment available to the movie industry. |
|
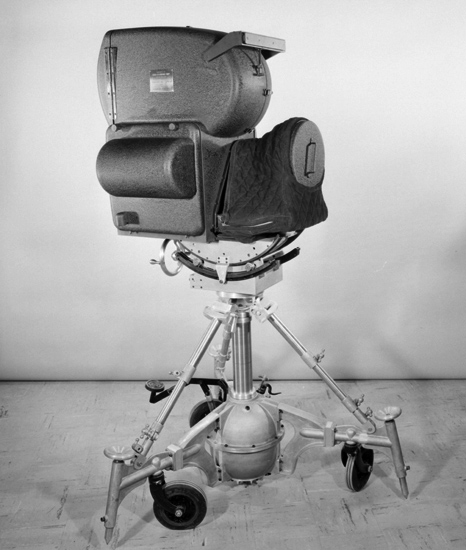 Blimped
Todd-AO camera with 128 dgr "Bug Eye" lens. Blimped
Todd-AO camera with 128 dgr "Bug Eye" lens.In November 1955, a month after the premiere of “Oklahoma!” the Todd-AO Corporation rented stage 3 at the Kling studios in Hollywood and converted a large sound stage into a mixing, dubbing and scoring stage for the films to be made in the process. The first film they worked on was “Around the World in 80 Days”. After the Rivoli opening, premieres followed in Los Angeles, Chicago and in San Francisco. Nearly two Todd-AO installations opened every month throughout 1956. One of the first demonstrations of Todd-AO in Germany was at the Photokina exhibition in Köln on 29 September 1956. Around 1958 American Optical sold their Todd-AO shares and at about the same time, 20th Century Fox invested in the process to film their major productions in 65mm. When "South Pacific" [the third Todd-AO feature] opened, the world of entertainment was shattered the 21 March 1958 by the news of Mike Todd's tragic death. His plane had crashed in a storm 35 miles southwest of Grants in New Mexico. Mike Todd left us a large format process carrying his name. Thanks to his determination to perfect audience participation, millions of moviegoers have enjoyed large bright pictures on the big screen with 6-track stereo for 5 decades. He biggest triumphed, though, was winning the 1956 best film Oscar for "Around the World in 80 Days". The heydays of 70mm films were in the 1960s and the Todd-AO camera division was busy throughout the decade with an average of one film photographed in the process each year. From 1970, use of 65mm cameras declined dramatically. With little demand for 65mm photography, the Todd-AO camera division developed new Academy Award winning anamorphic lenses for 35mm photography, named “Todd-AO 35”. Todd-AO photography finally came to an end in 1992 with the stunning non-verbal film, “Baraka”. Including other 65mm processes, less than 50 movies were filmed in 65mm. |
|
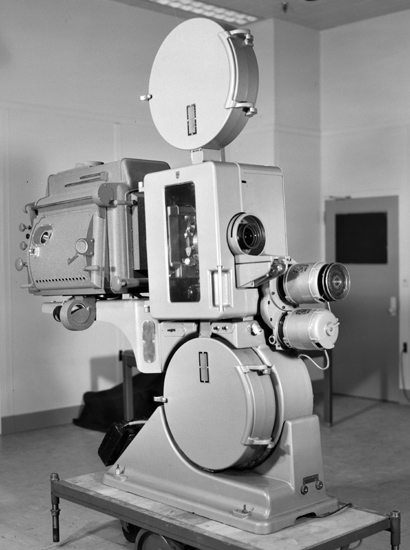 Todd-AO
"all purpose" 70mm projector installed at American Optical Research Center's
"half-scale" Todd-AO demonstration theatre. Todd-AO
"all purpose" 70mm projector installed at American Optical Research Center's
"half-scale" Todd-AO demonstration theatre. Despite the fact that 65mm was largely abandoned 50 years ago, the use of 70mm prints, enlarged from 35mm film, was widely used until the arrival of digital sound in 1992. These "blow-ups" were very popular thanks to the outstanding 6-track magnetic Dolby Stereo sound. In fact, cinemas showing 70mm prints often out grossed their 35mm counterparts. It was always a major draw for a cinema to be able to write “presented in 70mm” on the marquee. More than 350 films were enlarged to 70mm film. During the 1990s only “Far and Away”, “Baraka” (Todd-AO), “Hamlet” were produced, photographed and released in 70mm. In recent years “Samsara”, “The Master”, “The Hateful Eight”, “Dunkirk”, “Murder on the Orient Express” and "Tenet" have all been produced with Panavison and IMAX’s large format cameras and lenses. Some cinemas like the Schauburg in Karlsruhe is keeping 70mm alive. Once a year an audience from Switzerland, Portugal, Holland, England, Sweden, Austria, France and Denmark are coming to Karlsruhe to see something very special. Why? Because, on this screen, the Todd-AO is shown in its full glory. Breathtaking - in the splendor of 70mm. I know you appreciate this cinema and also realize, how rare it is to see Todd-AO - as it was meant to be seen – in a cinema. The Todd-AO film library is also available in a way Mike Todd never would have imagined. Today you can watch Todd-AO on BluRay, in letterbox and wonderful 6-track digital sound, in the comfort of your living room, or on portable players in any location you could wish for. Which is of course ironic, since wide curved screens originally was developed to get the audience OUT of their homes and INTO the cinema. Today it is the other way around. Only 18 feature films were filmed in the Todd-AO process. The tag line “Filmed in Todd-AO” on the cinema marquee, always meant the finest quality in movie making. For many people, those films left an ever-lasting impression, because it was indeed; “The Greatest Show in Todd-AO” |
|
Todd-AO at a Glance |
|
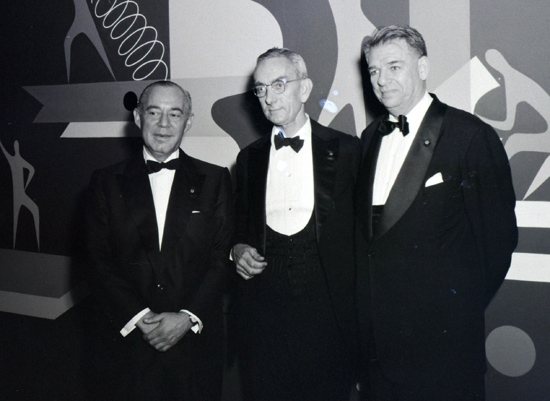 Dr.
Brian O'Brien flanked by Rodgers & Hammerstein II at the Rivoli Theatre on
opening night of Todd-AO and "Oklahoma!" October 1955. Dr.
Brian O'Brien flanked by Rodgers & Hammerstein II at the Rivoli Theatre on
opening night of Todd-AO and "Oklahoma!" October 1955.
Todd-AO is the dream of Michael Todd, plus the technical skills of the American Optical Company whose research staff headed by Dr. Brian O'Brien, jointly succeeded in developing:
|
|
| Go: back - top - back issues - news index Updated 22-01-25 |
